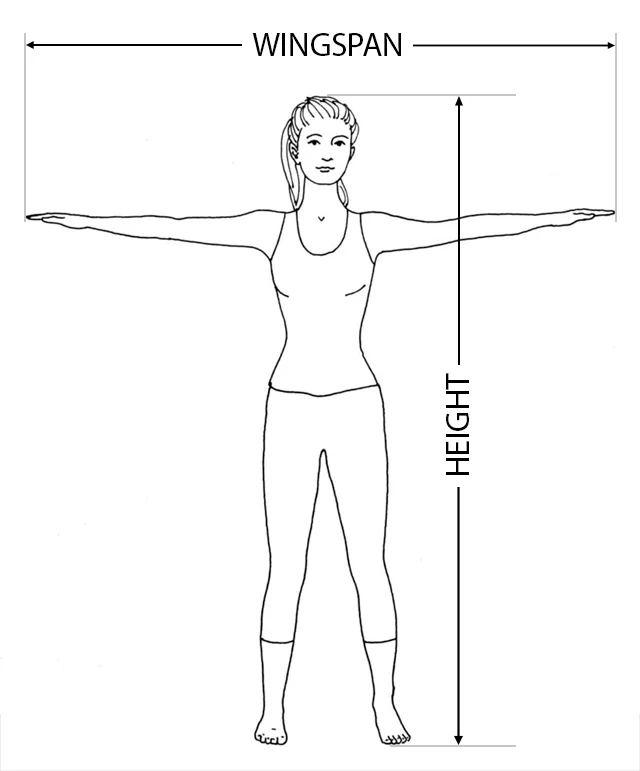
The Ape Ratio, also known as the Ape Index or wingspan to height ratio, is a numerical measure that compares an individual's wingspan (the distance from fingertip to fingertip when arms are fully extended) to their height.
Ape index formula
The Ape index is calculated using the following formula:
Ape index = Wingspan / Height
This index is expressed as a numerical value, and it can be either positive, negative, or equal to 1, depending on whether the wingspan is greater than, less than, or equal to the height.
Ape index result interpretation
The interpretation of the wingspan to height ratio, often referred to as the Ape Ratio or Ape Index, is crucial in understanding an individual's body proportions, particularly in the context of activities such as rock climbing. Here's how to interpret the results based on the calculated ratio:
Positive Ape Ratio (> 1)
A positive Ape Ratio indicates that the wingspan is greater than the height.
Individuals with a positive Ape Ratio tend to have a longer reach, potentially making them well-suited for climbing styles that involve reaching distant holds, making dynamic moves, and spanning gaps. This can be advantageous in routes or bouldering problems that require extended reaches.
Negative Ape Ratio (< 1)
A negative Ape Ratio suggests that the wingspan is shorter than the height.
Climbers with a negative Ape Ratio may excel in more technical and precise climbing styles. While they may have a shorter reach, they might compensate with enhanced balance, precision, and intricate movements. This can be advantageous in routes that demand careful footwork, balance, and controlled movements.
Ape Ratio = 1
An Ape Ratio of 1 indicates that the wingspan is equal to the height.
Individuals with an Ape Ratio of 1 have proportionate body dimensions. They may not have a significant advantage or disadvantage in terms of reach and climbing style based solely on their Ape Ratio. Other factors like technique, strength, and experience play a crucial role in their climbing performance.
It's important to note that while the Ape Ratio can provide insights into potential advantages or strengths in climbing, it is just one of many factors influencing climbing performance. Climbers should consider a holistic approach, incorporating technique, strength, flexibility, and experience in their training and climbing strategies. Additionally, individual preferences and styles may vary, and success in climbing is influenced by a combination of factors beyond body proportions.
Where the ape index is important
The ape index holds significance in various fields and activities where body proportions can impact performance or have specific applications. Some notable areas where the ape index is important include:
Rock Climbing and Bouldering
In climbing, the ape Index is crucial for understanding a climber's reach, ability to span gaps between holds, and overall climbing style.
Climbers with a positive ape Index may have an advantage in reaching distant holds and making dynamic moves, while those with a negative ape Index might excel in technical and precise climbing.
Basketball
A player's wingspan can be important in basketball, especially for positions like center or forward where rebounding and shot-blocking are crucial.
Players with a positive ape Index may have an advantage in reaching for rebounds and contesting shots due to their longer wingspan.
Swimming
In swimming, the ape index can affect stroke efficiency and overall performance.
Swimmers with a positive ape index might have a longer reach in strokes like freestyle and butterfly, potentially impacting their stroke technique and speed.
Combat Sports
In martial arts and combat sports, reach can be a significant factor in strategizing and executing techniques.
Fighters with a positive ape index may have an advantage in striking range, while those with a negative ape index might focus on close-quarters techniques and grappling.
Design and Ergonomics
In the design of tools, equipment, and workspaces, considering body proportions is essential for ergonomic efficiency.
Designers may use the ape index data to create products or spaces that accommodate a range of body types, ensuring comfort and usability.
Astronaut Selection
In space exploration, body proportions can influence the selection of astronauts for certain tasks.
Astronauts with a positive ape index might be better suited for tasks requiring long reaches in the confined space of a spacecraft or during extravehicular activities.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Understanding body proportions is relevant in physical therapy to tailor rehabilitation programs.
Therapists may consider the ape index when designing exercises or interventions for individuals with specific body proportions or mobility challenges.
Ape index of some athletes
| Name | Sport | Height | Wingspan | Ape index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Michael Jordan | Basketball (NBA) | 6′ 6″ | 6′ 11″ | 1.064 |
| Kobe Bryantn | Basketball (NBA) | 6′ 6″ | 6′ 11″ | 1.064 |
| Shaquille O'Neal | Basketball (NBA) | 7′ 1″ | 7′ 7″ | 1.071 |
| Muhammad Ali | Boxing | 6′ 3″ | 6′ 6″ | 1.04 |
| Mike Tyson | Boxing | 5′ 10″ | 5′ 11″ | 1.014 |
| Manny Pacquiao | Boxing | 5′ 5″ | 5′ 7″ | 1.031 |
| Michael Phelps | Swimming | 6′ 4″ | 6′ 7″ | 1.039 |
| Ian Thorpe | Swimming | 6′ 5″ | 6′ 5″ | 1 |